Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 was a historic event in astronomy that took place in July of 1994. It was a comet that collided with Jupiter, which was the first time in history that astronomers were able to observe a collision between two solar system bodies. Here’s what you need to know about this incredible event.
Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 was discovered in March of 1993 by a team of astronomers, including husband and wife duo Eugene and Carolyn Shoemaker and David Levy. The comet was unique in that it was in orbit around Jupiter rather than the sun. This was believed to be due to a close encounter with Jupiter in 1992 that caused the comet to be captured by Jupiter’s gravitational pull.
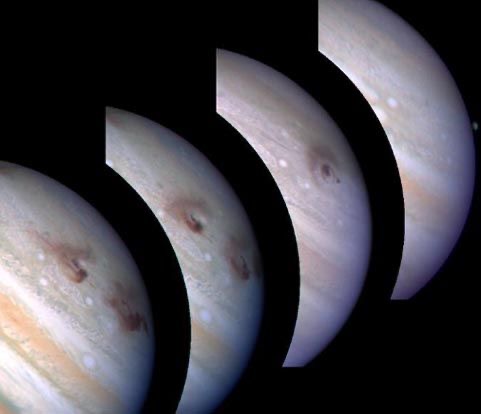
In July of 1994, Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 collided with Jupiter. The comet had broken up into 21 fragments, which collided with Jupiter over a period of several days. The impact was visible from Earth through telescopes and was a spectacular event for astronomers to witness.
The impact of Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 on Jupiter was significant. The energy released by the impact was estimated to be equivalent to several million nuclear bombs. The impact also caused massive storms on Jupiter, with one storm being observed that was larger than the entire Earth.
The study of the impact of Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 on Jupiter provided valuable insights into the dynamics of our solar system. It allowed astronomers to study the composition of comets and their behavior in space, as well as the behavior of planets and their moons.
In the end, Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 was a historic event in astronomy that took place in July of 1994. It was a comet that collided with Jupiter, which was the first time in history that astronomers were able to observe a collision between two solar system bodies. The impact was visible from Earth and provided valuable insights into the dynamics of our solar system.
